Information technology security, or cyber security, is a set of strategies meant to protect an organization’s computers, software, and data, from unauthorized access. The purpose of IT security is to maintain the integrity and confidentiality of your company’s sensitive information and to prevent the disruption of your company’s services.

Email is the most common method used by attackers to get sensitive information or deliver malware onto a computer or network. Hacks are surprisingly commonplace. In 2014, nearly half of all American adults had some form of data stolen from corporate servers in a 12-month span, according to CNN. Credit cards, telephone numbers, and login credentials are falling into the hands of hackers who can use that information to access linked accounts.
Corporate data breaches have harmed millions of people. Hackers have gotten into the servers of some of the largest companies in the world, including Yahoo!, LinkedIn, and Tumblr, stealing passwords and credit cards. While hackers can invade your business website directly, the most common way to hack your business is to hack business email accounts in order to gain access to website database passwords. Email is the primary attack vector for hacking and fraud, and the situation is only getting worse. From 2017 to 2018, email-based attacks on businesses increased 476%, according to the most recent threat survey by the cybersecurity firm Proofpoint.
The FBI reports there are 14,000 email scams each year worldwide, costing companies $12 billion annually. Recently, it was reported that Google and Facebook were scammed out of over $120 million by someone who sent forged contracts and invoices asking for payment. Or, in what is probably the most infamous example of phishing, in 2016, the campaign manager of Hillary Clinton’s presidential bid was fooled into clicking on a malicious link and entering his Google password. This exposed his entire Gmail inbox. Effects of a cyber attack can be very expensive. 53% of hacked companies reported that cyber attacks resulted in financial losses of more than $500,000. 38% reported that cyber attacks cost their company more than one million dollars!
Ransomware is also a significant problem. According to the Ponemon Institute, more than 4,000 Windows ransomware attacks occur every day in the US. Yet businesses in the US continue to use not only the insecure Windows operating system, but also insecure MS Exchange Email servers – leaving them wide open to expensive ransomware attacks.

Why Emails are Vulnerability to attack
As most email providers hold all of your messages on their servers, any hacker that is able to penetrate those servers will also have access to all of your information and the information of everyone else whose emails are stored on that server. The most recent and perhaps most serious breach of this kind is the Microsoft Exchange hack, though there is a long history of email server hacks, with victims including Yahoo, Sony, and even the NSA.
Despite how expensive email hacks can be, most business owners have no idea how email systems work or how to protect themselves from email attacks. We will therefore review how the Hestia email system works and how its programs have been carefully chosen to protect your business from hacker attacks.
How the Hestia Email System Works
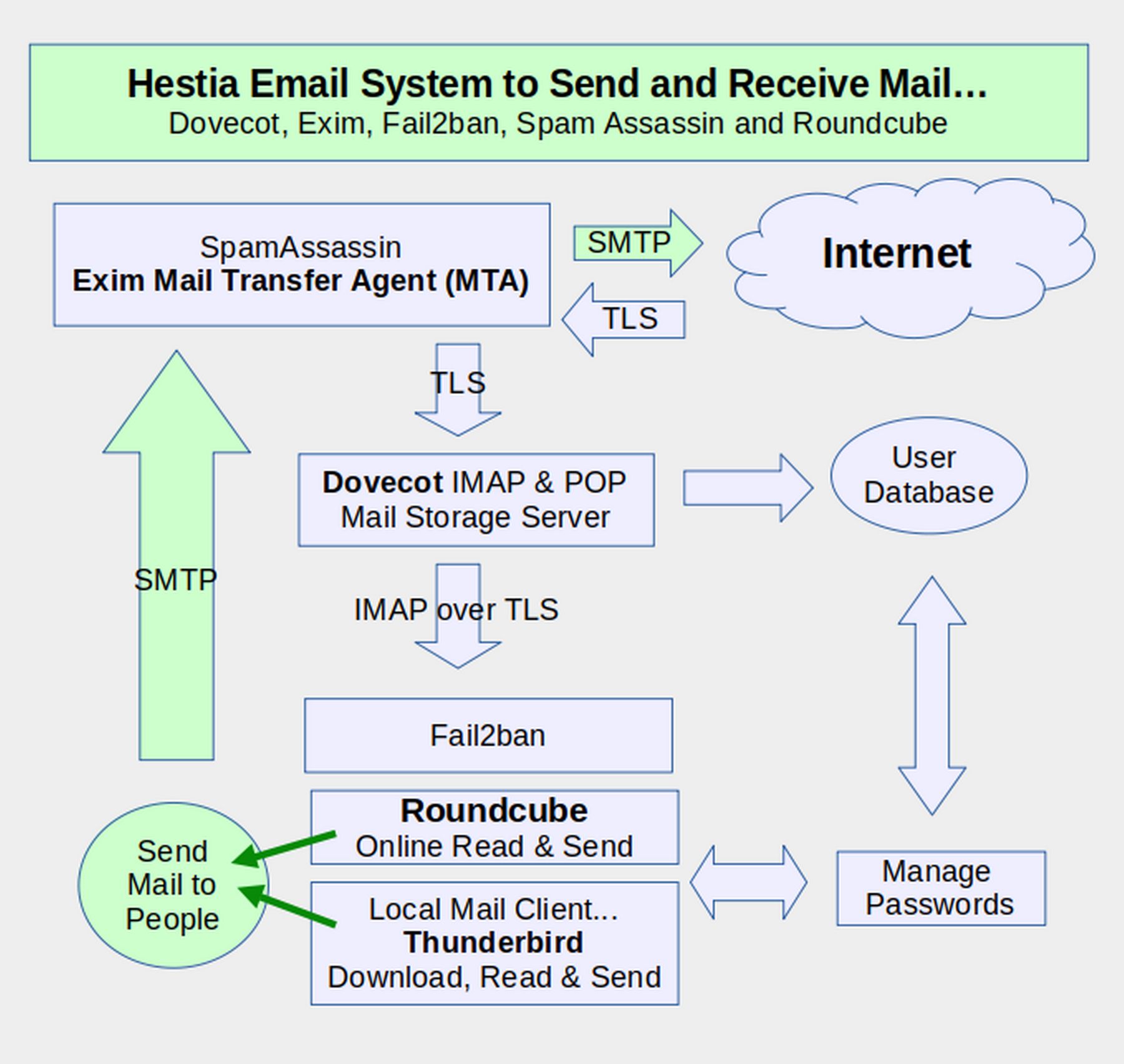
As you can see from the diagram below, there are a lot of different programs installed in Hestia that work together to help your business securely send and receive emails.
In the following articles, we will set up Hestia custom emails accounts which you can then read online by logging into a free open source program called Roundcube. We will then create a free encrypted email account using ProtonMail. We will then connect both of these accounts to a Thunderbird Mail Client which is installed on our LMDE home computer.
You can then read and sent emails either from your Home computer or by logging into your Roundcube account which is located inside of your VPS server.
However, there are several other components of the Hestia email system you should be aware of. The first of these is a Mail Transfer Agent (MTA) called Exim. Exim receives incoming emails from other servers and forwards them to a Mail Storage server called Dovecot.
Exim also receives outgoing mail from either Thunderbird or Roundcube and passes this mail out to other email servers on the Internet.
Exim is protected by a free open source Spam filtering program called Spam Assassin. The default Hestia Email system also protects Exim with a anti-virus program called Clam AV. However, because of the structure of the Linux operating system, and because Claim AV uses an entire Gigabit of RAM, we recommend not using Clam AV. Finally, Roundcube and Thunderbird are protected by an additional email filter called Fail2ban. Thankfully, Fail2ban uses very little RAM.
Note that all incoming emails are transferred through an encryption program called Transport Layer Security (TLS). Because this is not really a full end to end encryption program, we will explain how to also use a real end to end Email encryption program called ProtonMail. Going the other way, all outgoing emails are transferred using a program called Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP). SMTP can also be called Send Mail to People.
As you will see in a moment, Hestia also comes with an easy process to create a Lets Encrypt SSL certificate for your Roundcube Log in page. As all of the email programs used by Hestia are free open source programs, there is no need to pay monthly fees. They have all also been audited for security. The Hestia email system is therefore one of the most secure VPS control panel email systems in existence.
What’s Next?
Now that we understand the Hestia email system, in the next article, we will use Hestia to set up a custom business email account.

